Historical nuclear weapons stockpiles and nuclear tests by country
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historical_nuclear_weapons_stockpiles_and_nuclear_tests_by_country
This article shows various estimates of the nuclear weapons stockpiles of various countries at various points in time. This article also shows the number of nuclear weapons tests conducted by each country at various points in time.Nuclear weapons stockpiles[edit]
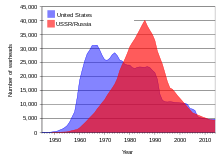
The United States nuclear stockpile increased almost exponentially between 1945 and 1965, but then began declining after peaking in 1966.[1] In 2012, the United States had several times fewer nuclear weapons than it had in 1966.[2] The Soviet Union joined the nuclear club in 1949 and had its nuclear stockpile increase very rapidly until 1986, when it peaked under Mikhail Gorbachev.[1]After the decrease of Cold War tensions and eventually the end of the Cold War, the Soviet and Russian nuclear stockpile decreased by over 80% between 1986 and 2012.[2] The U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons stockpiles are projected to continue decreasing over the next decade.[3]The United Kingdom joined the nuclear club in 1952 while France joined it in 1960. The British and French nuclear stockpiles peaked at about 500 nuclear weapons in 1981 and 1992, respectively.[1]
China joined the nuclear club in 1964 while its nuclear stockpile increased until the early 1980s, when it stabilized.[1] India joined the nuclear club in 1974, while Pakistan joined the nuclear club in the 1980s.[1][6] Both India and Pakistan currently have around one hundred nuclear weapons.[2] Pakistan's nuclear stockpile has been increasing at a very fast rate, and it is speculated that Pakistan might have more nuclear weapons than the United Kingdom within a decade.[7] South Africa successfully built six nuclear weapons in the 1980s, but dismantled all of them by the end of the 1990s after the end of apartheid.[8] North Korea joined the nuclear club in 2006 or before.[9][1] Without negotiations and "other proper measures", North Korea could increase its current nuclear weapons stockpile by several times by 2016.[10] A United States Defense Intelligence Agency report from 1999 projected that both Iran and Iraq will join the nuclear club and have 10-20 nuclear weapons in 2020.[11] However, it is worth pointing out that this report was written before the overthrow of Iraqi dictatorSaddam Hussein and before info indicating that Iraq already gave up its nuclear weapons program by 1999 was released.[11]
| Country | 1945 | 1950 | 1955 | 1960 | 1965 | 1970 | 1975 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2013[2] | Future projections |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 299 | 2,422 | 18,638 | 31,139 | 26,008 | 27,519 | 24,104 | 23,368 | 21,392 | 10,904 | 10,577 | 8,360 | 7,700 | 3,620 (for 2022)[3] | |
| 0 | 5 | 200 | 1,605 | 6,129 | 11,643 | 19,055 | 30,062 | 39,197 | 37,000 | 27,000 | 21,500 | 17,000 | 8,500 | 3,350 (for 2022)[3] | |
| 0 | 0 | 14 | 42 | 436 | 394 | 492 | 492 | 422 | 422 | 422 | 281 | 281 | 225 | 180 (for around 2025)[12] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 36 | 188 | 250 | 360 | 505 | 500 | 470 | 350 | 300 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 75 | 180 | 205 | 243 | 232 | 234 | 232 | 235 | 250 | 150-220 (for 2020)[11] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 20 | 31 | 42 | 53 | 63 | 72 | 80 | 80 | 65-85 (for 2020)[11] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0[9] | 1[9] | 3[9] | 7[9] | 14[9] | 28[9] | 44 | 90-110 | 50-70 (for 2020)[11] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0[9] | 3[9] | 6[9] | 0[9] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0[11] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0[9] | 4[9] | 13[9] | 28[9] | 38 | 100-120 | 150-200 (for 2021)[13] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0[9] | 0[14]-1[9] | 0[14]-2[9] | 0[14]-2[9] | 8[9] | 6-8 | 28-48 (for 2016)[10] | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10-20 (for 2020)[11] |
Even before the United States of America started the nuclear club in 1945, some countries (most notably Nazi Germany) unsuccessfully attempted to build nuclear weapons.[15]
Nuclear weapon tests[edit]
| Country | 1945-49 | 1950-54 | 1955-59 | 1960-64 | 1965-69 | 1970-74 | 1975-79 | 1980-84 | 1985-89 | 1990-94 | 1995-99 | 2000-04 | 2005-09 | 2010-14 | Cumulative total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All countries | 9 | 63 | 228 | 362 | 344 | 277 | 273 | 265 | 174 | 43 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2,055 |
| 8 | 43 | 145 | 198 | 230 | 136 | 96 | 84 | 71 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,032 | |
| 1 | 17 | 65 | 147 | 85 | 101 | 126 | 116 | 56 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 715 | |
| 0 | 3 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 19 | 32 | 37 | 51 | 41 | 12 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 210 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1[17] | 3 |
From the first nuclear test in 1945, worldwide nuclear testing increased rapidly until the 1970s, when it peaked.[16] However, there was still a large amount of worldwide nuclear testing until the end of the Cold War in the early 1990s.[16] Afterwards, the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty was signed and ratified by the major nuclear weapons powers, and the number of worldwide nuclear tests decreased rapidly.[16] India and Pakistan conducted nuclear tests in 1998, but afterwards only North Korea conducted nuclear tests—in 2006, 2009, and 2013.[18][16]


No comments:
Post a Comment